
The accuracy of metering pump has always been a concern of customers in the actual use of metering pump. This paper will combine some problems that some customers encounter in the practical application process, and give answers from the perspective of professional metering pump manufacturers, for your reference.
Accuracy concept of metering pump
Q:
What is the accuracy of the metering pump?
Answer:
The use of metering pump involves three aspects of accuracy.
1) Steady state accuracy of mechanical diaphragm metering pump: ± 2% of rated flow. If the measured 100% stroke flow of metering pump is 1000L / h, the allowable deviation of steady-state accuracy is ± 2% * 1000 = ± 20 L / h. The steady-state accuracy refers to the flow deviation obtained by calibrating the flow of the dosing pump and related systems at different time points without any adjustment and change.
2) Linear accuracy: ± 3% of rated flow. If the measured 100% stroke flow of metering pump is 1000L / h, the allowable deviation of linear accuracy is ± 3% * 1000 = ± 30L / h. Linear accuracy refers to the deviation between the measured flow and the best fitting value obtained by selecting different travel points eve
nly to calibrate the flow within the range of 10% ~ 100% of the travel of the metering pump
nly to calibrate the flow within the range of 10% ~ 100% of the travel of the metering pump
3) Repeat accuracy: ± 3% of rated flow. If the measured 100% stroke flow of metering pump is 1000L / h, the allowable deviation of repeat accuracy is ± 3% * 1000 = ± 30L / h. Repetitive accuracy refers to the flow deviation obtained by selecting a certain stroke point to calibrate the flow within the range of 10% ~ 100% of the stroke of the metering pump, then changing the stroke of the pump for a period of time, and returning to the original stroke point again to calibrate the flow.
Q:
What is the regulating ratio of the metering pump and what is the function of the regulating ratio?
Answer:
Regulating range and ratio of metering pump: the metering pump is similar to other adjustable equipment and has a regulating ratio parameter. The regulating ratio of the metering pump is 10:1, that is, within the range of 10% ~ 100%, the accuracy of the metering pump meets the requirements. In the range of less than 10%, it is usually a non adjustable sensitive area, so it is not required in the accuracy range.
Practical application problems
Q:
When we use the variable frequency metering pump, we encounter a problem that the flow is not accurate. The specific description is as follows:
Metering pump: 965l / h; lift: 4bar; pump head: PVC; 380V, 50Hz variable frequency motor,
Stroke: 5%; flow at 10Hz: 35-40l / h
According to the condition of this pump, whether the following calculation is correct
965l / h * 5% = 48.25l/h (50Hz). In the same proportion, 10Hz should be 9.65l/h, which is quite different from the actual 35-40l / h.
What's the operation of the variable frequency pump? Why is there such a big deviation?
Answer:
1. Whether the system has stable system back pressure when your company conducts site calibration. If there is no stable back pressure, just keep the outlet of the metering pump under normal pressure, or even the outlet is lower than the liquid level of the storage tank, the outlet flow deviation may be large
2. In addition, may I ask if you have a pressure gauge at the outlet of the metering pump when you are carrying out the flow calibration, and what is the system pressure?
3. During the flow calibration of metering pump, it is necessary to maintain a pressure difference of at least 0.2MPa between the outlet and inlet of metering pump to ensure that the metering pump meets the relevant accuracy requirements.
4. In order to ensure that the pump parameters reach the rated parameters, the actual flow of each metering pump is greater than the rated parameters of the data sample. I randomly selected the test data of three mc1000pr in one contract of your company, among which the actual maximum flow of 001 pump is 1073.8 L / h. An increase in the maximum also increases the flow at low stroke.
Q:
If it's still this pump. If I turn the stroke to 10%, it's 1073.8 * 10% = 107.38l/h at 50Hz
I would like to ask, what is the precision deviation at this time, which is ± 3% of 107.38l/h or still ± 3% of 1073.8
At the same time, whether the flow calculation between 10% - 100% is: flow = (rated flow * stroke * frequency / 50) ± 3%
We need to program when we do the program.
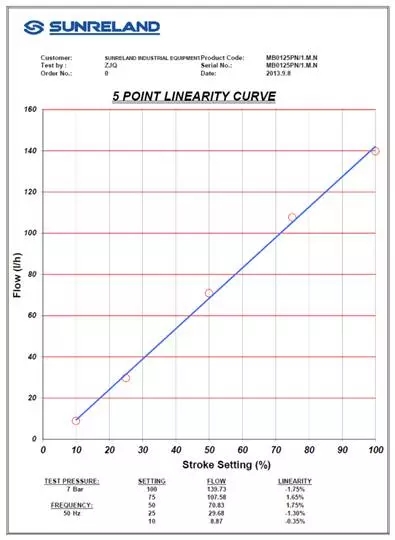
Answer:
The diagram above shows the relationship between flow and stroke of metering pump.
The circle point in the figure is the measured flow value, and the blue line is the best result after the fitting calculation, as can be seen from the above figure.
1) The relationship between flow and stroke does not pass through the origin, so it cannot be calculated according to the linear relationship of 0 ~ 100% passing through the origin. The equation has intercept in both horizontal and vertical axes.
2) The ± 3% deviation is ± 3% of rated flow, i.e. ± 3% * 1073.8 = ± 32.2 L / h. The deviation value is the deviation between the measured value and the best value.
3) If there are strict requirements for the dosage of chemicals on site, the actual use of chemicals is required. Under the actual conditions of the dosing system, there is a stable system back pressure to calibrate the flow of the metering pump. Then according to the measured value of different stroke, draw the best fitting line, as the regulation guide of daily operation.
4) If the frequency conversion control is needed, the flow calibration should be carried out under different frequency conditions, so as to get the flow stroke relationship diagram under different frequency.

